Agent of Record vs Employer of Record: Key Differences
Global hiring can sometimes feel like decoding: AOR, EOR, PEO, and other terms. Where do you even start?
If you’re planning to expand globally, you’ve probably already encountered two terms: Agent of Record (AOR) and Employer of Record (EOR).
Although they sound interchangeable, they aren’t, and choosing one over another can lead to legal issues, misclassification and even government penalties.
So how do you know which model is right for your business goals?
Read on to learn more about Agent of Record vs Employer of Record to see which option supports your global growth the best.
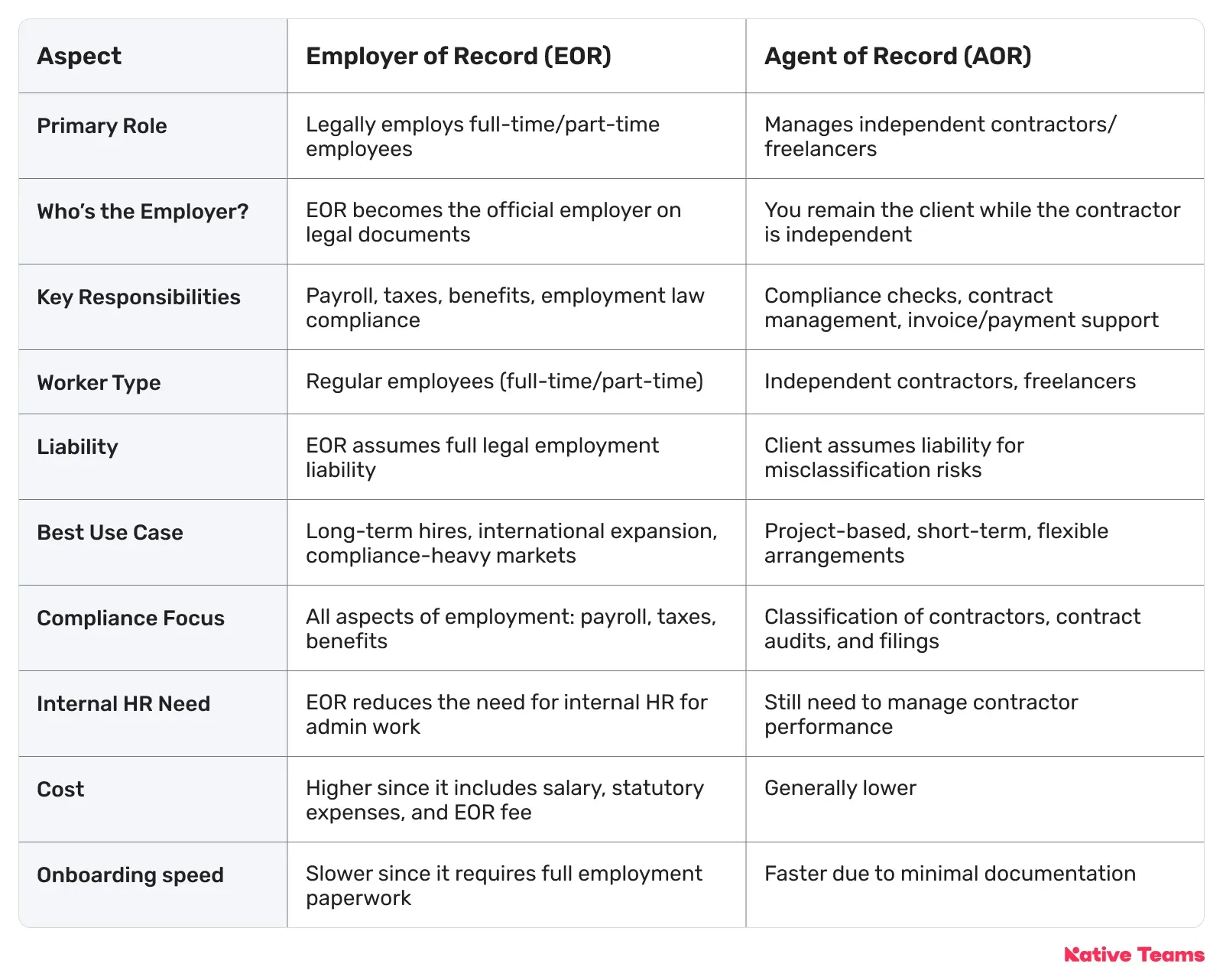
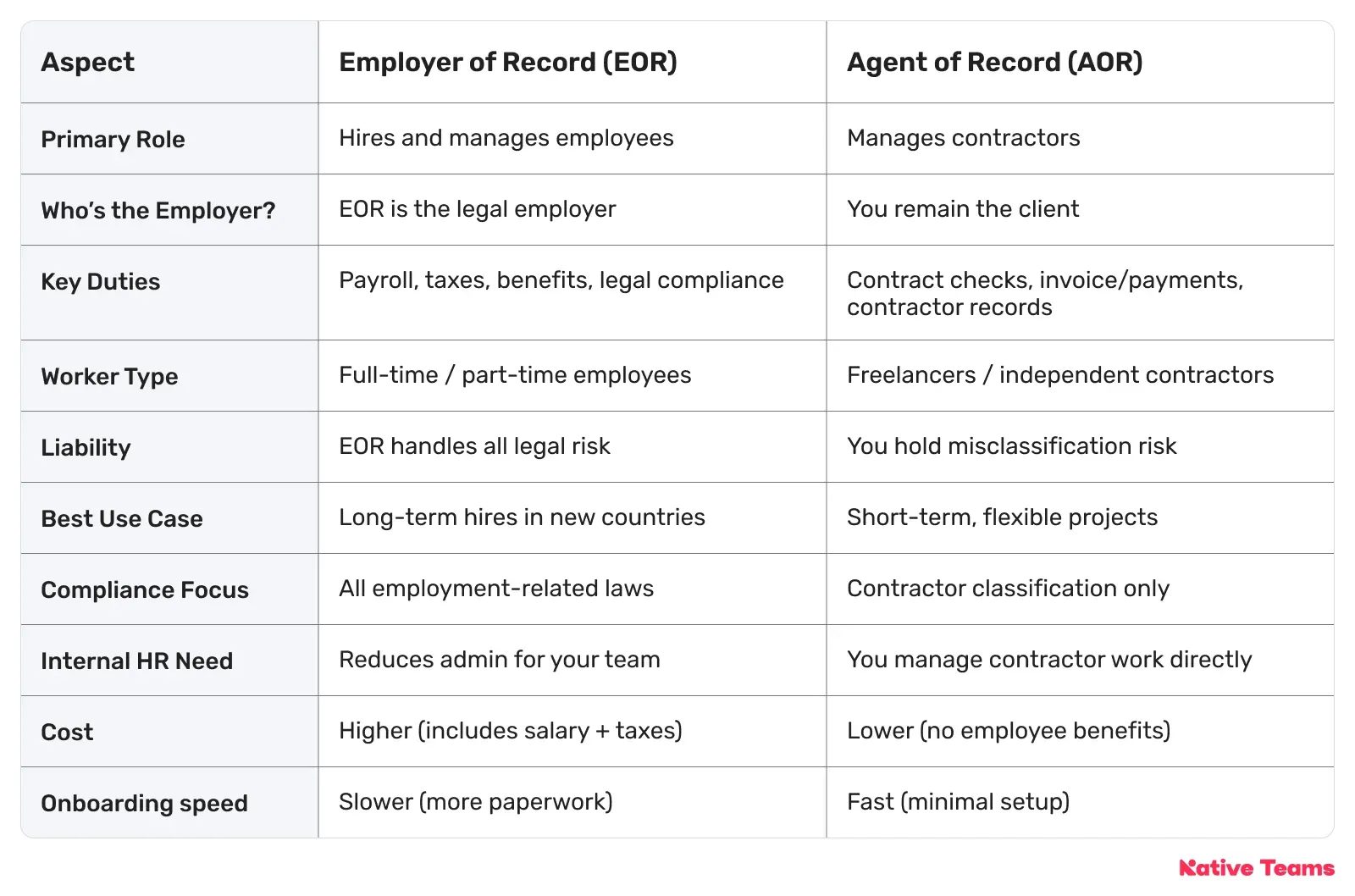
Agent of Record vs Employer of Record: A quick comparison
Let’s check the main areas of difference between AOR and EOR before we dive deeper.
What is Agent of Record (AOR): Overview and key functions
An Agent of Record, or AOR, is a third party you trust to handle admin, contracts, and compliance for your independent contractors.
AORs manage relationships with independent contractors, freelancers, and, in some sectors, represent clients with insurance providers, benefits brokers, or other specialised service vendors.
Key functions of an AOR:
- Intermediary role: An AOR serves as the single point of contact between the client company and independent contractors (or other service providers), handling the flow of information, contracts, and regulatory forms.
- Administrative support: They take on crucial back-office functions, including drafting and managing contracts, onboarding contractors, processing payments and invoices, and collecting compliance documentation.
- Compliance management: An AOR specialises in regulatory compliance for engaging contractors, ensuring that tax filings, right-to-work checks, and labour law requirements are followed.
- Risk mitigation: As the AOR is legally responsible for many compliance aspects, it absorbs much of the liability associated with contractor misclassification or administrative errors.
Contract and payment handling: The AOR manages payment processes and maintains audit-ready records for tax and labour inspections.
Why companies use AORs: 4 main benefits
- Scalability: As businesses expand globally and in terms of the contractor number, administrative tasks become complex. AORs streamline engagement with a growing freelancer or contractor workforce.
- Focus: By delegating non-core functions like compliance and contractor management to an AOR, you can focus on your primary business activities.
- Global expansion: AORs know varying regional and international labour and tax laws. They ensure workers are properly classified and compliant, which is crucial if you have a global workforce.
- Peace of mind: With AORs managing administrative and legal aspects, businesses reduce their exposure to contractor misclassification claims or regulatory penalties.
What legal protections and responsibilities does an AOR hold in contractor relationships?
An AOR acts as an intermediary between the client company and the independent contractors.
Key legal responsibilities of an AOR include:
- Managing contractor compliance,
- Ensuring the correct classification of workers, and
- Handling administrative duties such as contracting, invoicing, and payments on behalf of the client.

An AOR reduces the client's liability risks, especially related to worker misclassification.
It ensures freelancers and contractors are properly classified under local labour and tax laws, maintaining compliance with all regulatory requirements.
They stay updated with changing labour laws and contractor classification guidelines and take on administrative burdens such as contract management and compliance audits.
Thus, they are protecting you from fines or legal penalties in case of non-compliance.
The legal protections the AOR receives come through clearly defined agreements with the client company.
These agreements outline the scope of their responsibilities, liabilities, and indemnity clauses.
By assuming these administrative and compliance duties, the AOR provides the client with an added layer of risk mitigation and accountability.
However, the AOR doesn’t become the legal employer.
You maintain ownership of the project and worker relationship, but delegate the administrative and compliance tasks to the AOR to reduce operational and legal risk.
What is an Employer of Record: Overview and key functions
An Employer of Record (EOR) is a 3rd-party organisation that legally employs workers on behalf of your company in a specific country or jurisdiction where you don’t have a registered legal entity.
As a result, an EOR helps you simplify global expansion and minimise administrative and legal complexities.
Key functions of an EOR:
- Legal employer status: The EOR assumes the role of the official employer in the host country. It acts as the legal entity for employee contracts, tax documents, and government registrations. This means the employee's labour relationship, payroll filings, and statutory employment compliance are officially under the EOR's responsibility.
- Payroll processing and tax withholding: The EOR manages all payroll functions, including salary disbursement, tax withholding, social security contributions, and other mandatory statutory deductions in compliance with local tax regulations.
- Benefits administration: It administers employee benefits according to local laws, including mandatory social security, health insurance, pensions, paid leave, and other statutory or voluntary benefits.
- Employment compliance: The EOR ensures that employment contracts comply with local labour laws, including working hours, minimum wages, termination procedures, severance payments, and workplace safety.
- Risk mitigation and liability management: By being the legal employer, the EOR assumes full employment-related liability, reducing your company’s exposure to risks such as labour disputes, tax audits, fines, or lawsuits related to local employment laws.
- Support for work permits and visas: Many EORs assist in securing work permits, visas, and immigration compliance for foreign employees.
- Ongoing employee management support: While the EOR handles all employment administration, your company retains control over the employees’ daily tasks, performance management, and business direction.
Why companies use EORs: 5 main benefits
- Global expansion without local entity setup: When a company wants to enter a new international market quickly but does not yet have or wish to establish a local legal presence.
- Hiring full-time or long-term employees: Especially in markets with strict employment laws, where managing compliance independently is complicated and risky.
- Compliance-heavy environments: Countries with intense regulatory requirements for payroll, taxes, labour rights, and benefits.
- Reducing legal and administrative burden: Businesses benefit by offloading the administrative load and legal liabilities associated with employment to a trusted third party.
- Speed and flexibility: Enables rapid onboarding of employees in foreign jurisdictions, often within a matter of weeks.
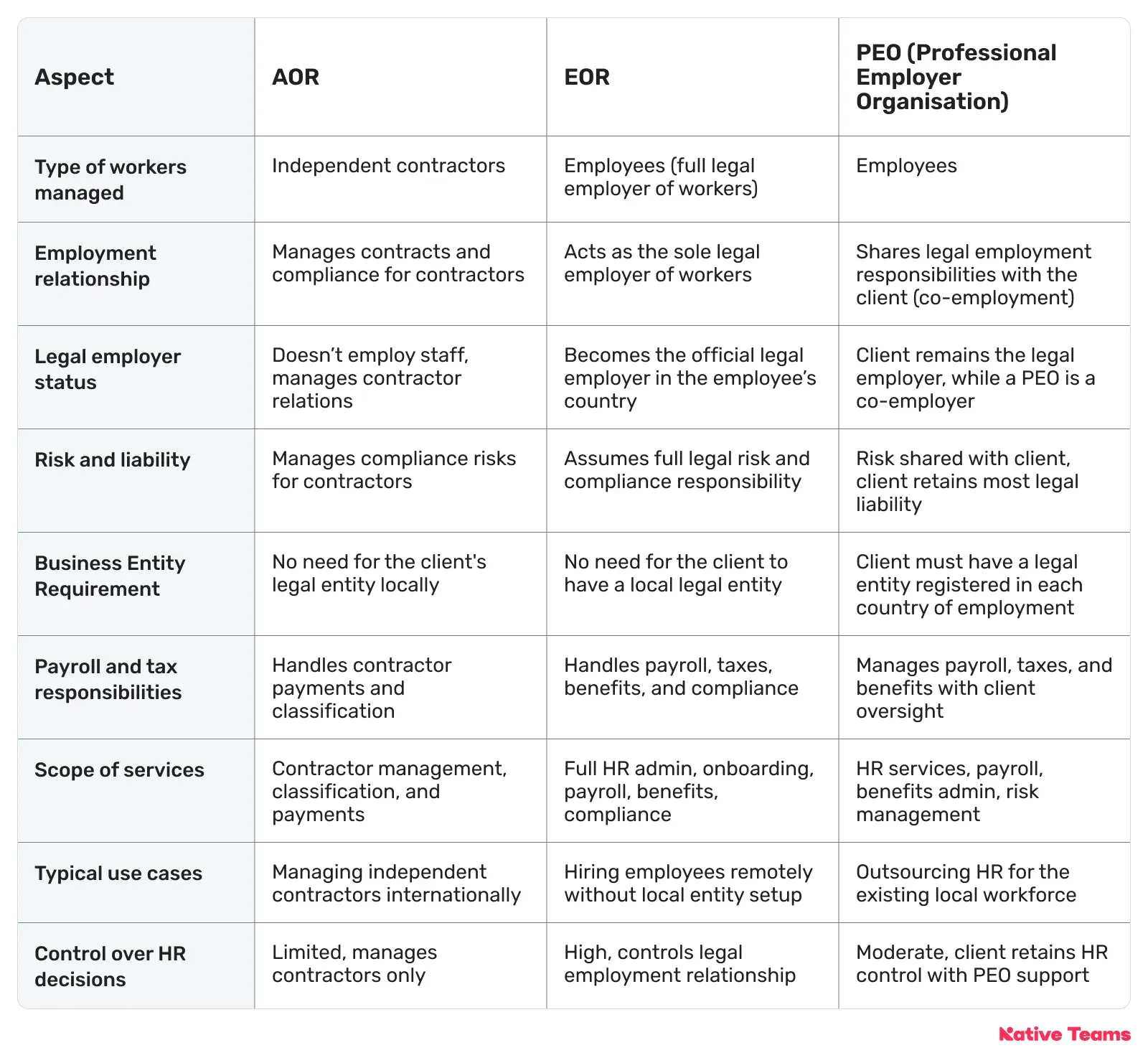
And what about PEO?
Remember the acronyms from our blog intro? PEO is the one that we simply can’t skip since it’s often interchanged with AOR and EOR, whereas the reality is quite different.
So, let’s recap!
- An AOR focuses on managing independent contractors.
- An EOR acts as the full legal employer, which is particularly useful for international hiring without local entities.
- A PEO offers co-employment HR outsourcing where the client retains legal employment but outsources HR services and shares liability.
And now, getting back to our main topic.
Agent of Record vs. Employer of Record: How do they handle international workforce regulations?
An AOR and EOR differ significantly in how they handle international workforce regulations, primarily due to their distinct roles and legal responsibilities in managing contractors versus employees.An AOR primarily supports compliance related to engaging independent contractors internationally.
It is an intermediary that manages classifications, contracts, and payments to ensure legal compliance with contractor regulations.
However, the client company retains most of the employment-related legal risk as the contractors remain independent.
This model offers high flexibility and is cost-effective for project-based, short-term engagements globally.
On the other hand, an EOR legally employs workers on behalf of a client company in foreign jurisdictions where the client has no legal entity.
The EOR assumes full responsibility for compliance with local employment laws, payroll, benefits administration, tax withholding, and employment contracts.
As a result, this model greatly reduces legal compliance risks for the client.
It is optimal to hire full-time or part-time employees long-term in markets with complex labour laws.
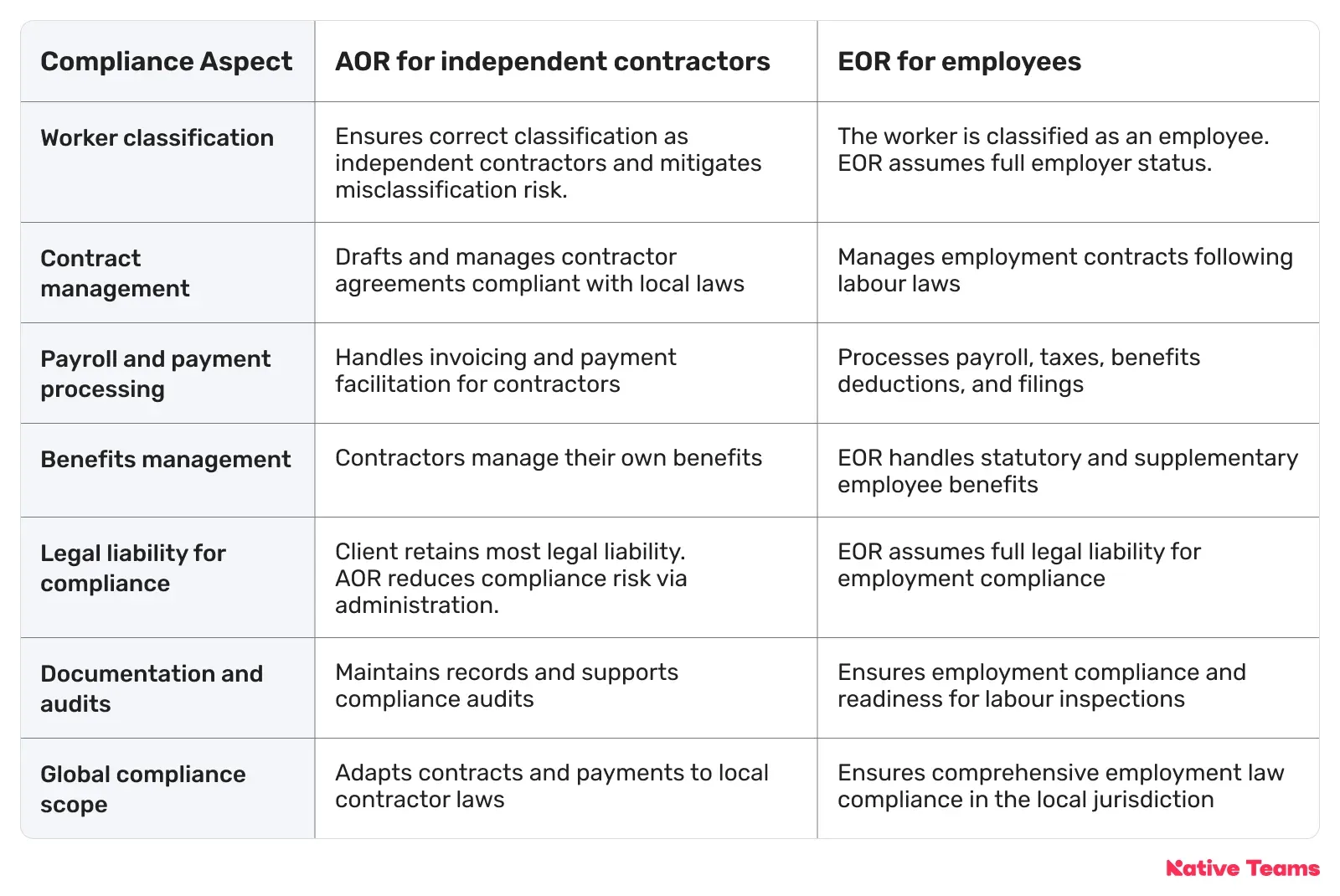
Agent of Record vs. Employer of Record: How do they ensure compliance?
An AOR safeguards compliance by managing the administrative and legal aspects of engaging independent contractors without becoming the legal employer.
An EOR, meanwhile, assumes full employment compliance responsibility by legally employing workers on behalf of the client.
This way, it provides a more structured and risk-mitigated solution for managing full-time or part-time employees internationally.
An AOR ensures compliance for independent contractors by focusing on proper worker classification, contract management, and payment processing in adherence to local contractor laws.
The AOR:
- Reviews and verifies that contractors are legally classified as independent,
- Drafts compliant contracts according to regional labour laws,
- Manages invoicing, and
- Processes payments to ensure timely and accurate compensation.
It also maintains audit-ready documentation, performs ongoing compliance monitoring, and mitigates risks related to worker misclassification.
However, the client is responsible for the contractors' actual work and engagement.
You can hire freelance or project-based contractors flexibly, ensuring regulatory compliance without the AOR assuming legal employer liability.
And how about an EOR?
It handles compliance for employees by legally becoming the employer on record in the relevant jurisdiction.
The EOR assumes full responsibility for all employment-related compliance, including:
- Payroll processing,
- Tax withholding,
- Benefits administration,
- Employment contracts,
- Local labour law compliance, and
- Offboarding if necessary.
The final verdict: Agent of Record vs Employer of Record: Which one should you choose?
Choosing between an AOR and EOR depends on your workforce structure, business needs, and compliance requirements, especially when operating across borders.
An AOR can be a good choice when you want to scale a contractor workforce without taking on full employment obligations.
On the other hand, choose an EOR when hiring employees in a new country and when you need full compliance and risk mitigation without setting up a business entity.
What if we told you that there is an EOR solution that enables you to hire full-time employees and contractors under one roof?
Enter, Native Teams!
Native Teams: An all-in-one solution for hiring globally
Native Teams is an EOR and PEO provider that helps you compliantly hire, pay, and manage an international workforce across 85 countries.
How do we combine AOR and EOR solutions?
✨ Contractor compliance and payments: Native Teams streamlines the engagement of independent contractors and freelancers by managing contracts, payment processing, and ensuring tax compliance across borders.
Contractors can easily generate invoices and get paid in their local currency, with all compliance documentation handled through the platform.
✨ Risk reduction: By acting as the intermediary, we help you reduce the risk of worker misclassification and ensure all contractor engagements align with local laws. This is especially valuable for companies scaling a diverse, project-based workforce internationally.
✨ Effortless onboarding: We guide you through onboarding, managing contracts, compliance documentation, and cross-border payments with minimal administrative burden
✨ Legal employer in over 85 countries: We act as the legal employer for your international workers, handling all aspects of employment, including:
- Contracts,
- Payroll,
- Tax filings,
- Social security contributions, and
- Employee benefits administration.
✨ Full compliance and risk mitigation: Native Teams ensures compliance with regional labour laws, manages statutory employee benefits, and takes on employer liability, protecting your company from costly legal risk.
✨ Global payroll and benefits: You can pay employees and contractors in multiple currencies, automate payroll, and provide localised benefits per country regulations.
Ready to discover more about how we can help?
Book a free demo today to see how you can make international hiring and payments seamless regardless of the worker type.
